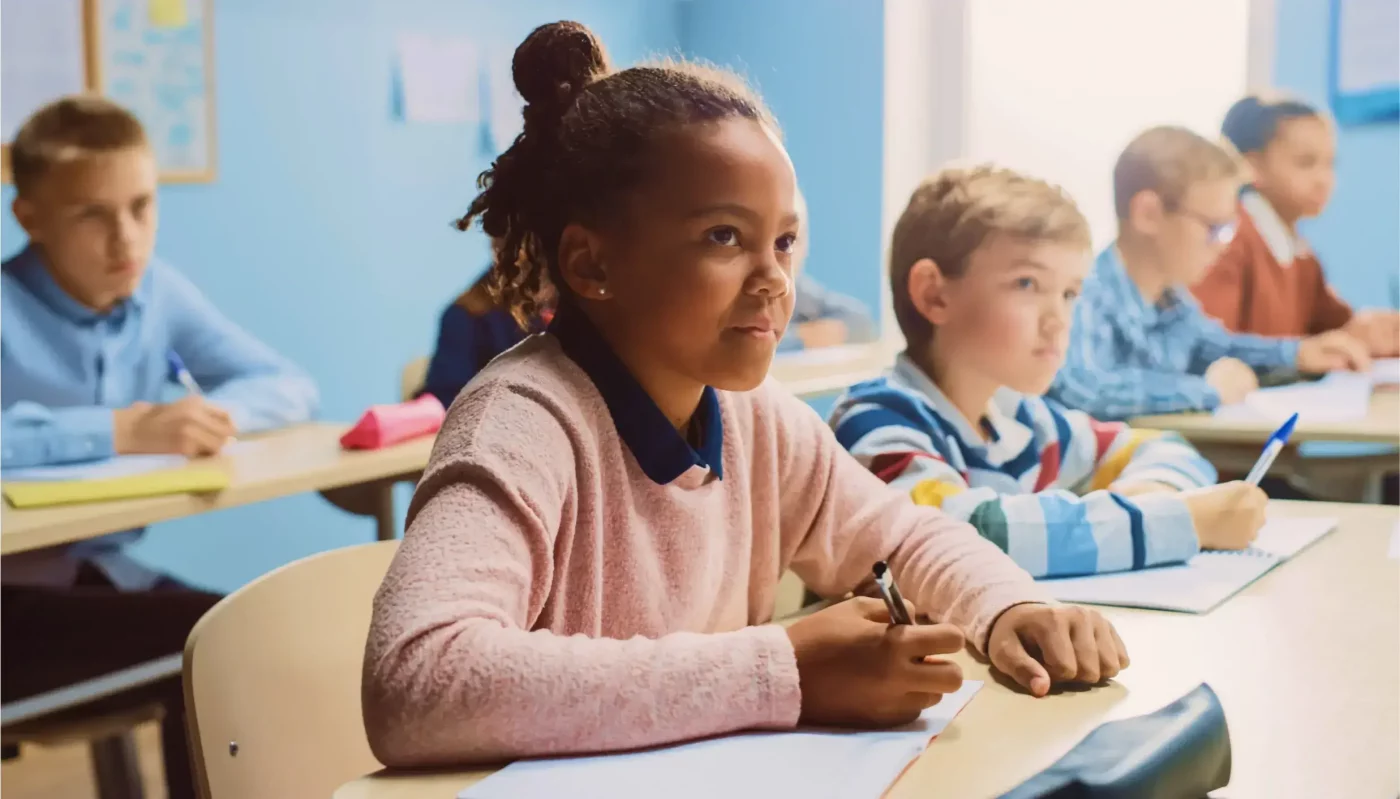
The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risk (MCPER), within the College of Education at The University of Texas at Austin, is a collaboration of researchers from multiple disciplines and sites. Our work has reached more than 2 million students.

Our Partners
We collaborate with a distinguished, interdisciplinary group of experts from a range of fields in our research and technical support efforts.




https://meadowscenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/smu.png
https://meadowscenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/texas-university.png
https://meadowscenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/utah-state.png
https://meadowscenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/boston-university.png
https://meadowscenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/children-learning-institute.png
https://meadowscenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/dell-childrens.png

